我院杨学弦副教授以“Effects of doping concentration on bond length and bond energy studied by Raman shift”为题在应用物理类国际权威期刊Applied Physics Letters上发表最新研究成果。基于其本人前期建立的计量声子谱学分析方法并结合拉曼频移组份效应实验,该研究工作构建了合金拉曼谱组份效应的定量解析新方法,为进一步的研究合金材料微观晶体结构和宏观物理性能提供了新的理论计算和实验分析新方法。
该研究工作以吉首大学为第一单位,杨学弦副教授为论文第一作者发表。研究工作得到了国家自然科学基金(No. 11602094)、新加坡教育部[No. RG70/20 (2020-T1-001-023)]、湖南省自然科学基金(No. 2022JJ30470)和国家公派留学基金(No. 202008430239)的资助。
Applied Physics Letters是美国物理学会(AIP)主办的老牌经典期刊,出版应用物理领域的重要研究成果,在国际上有很高的认可度和一定的影响力。
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0160714.
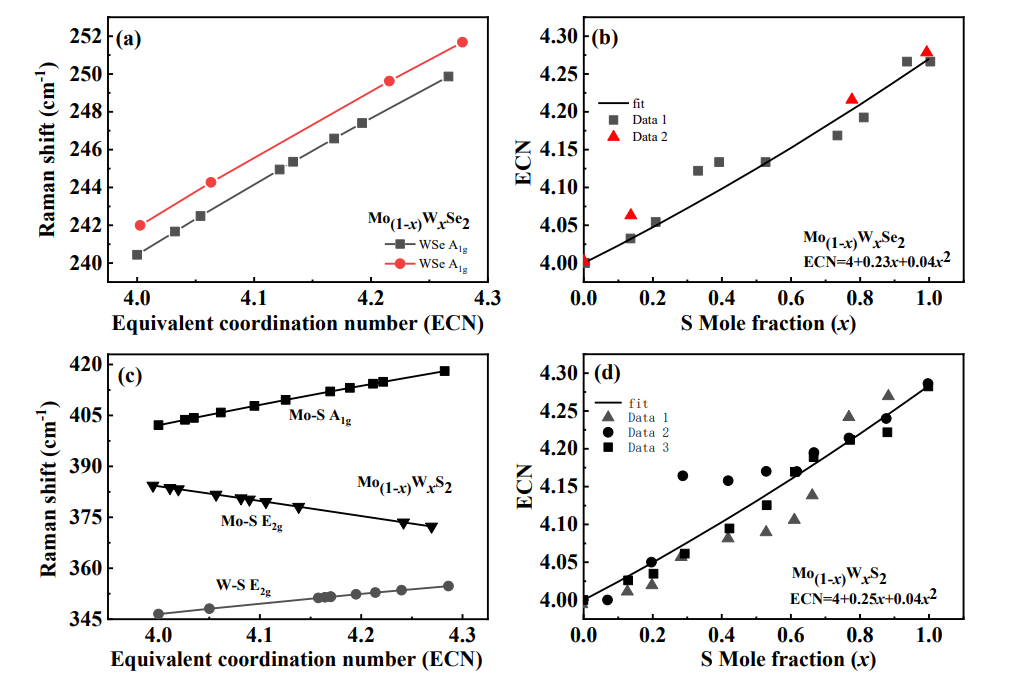
图1. (a) and (c) Relationships between Raman frequencies of the A1g and E2g modes and equivalent coordination number for Mo(1-x)WxSe2 and Mo(1-x)WxS2 monolayers. (b) and (d) Relationship between equivalent coordination number and doping concentration generated from (a) and (c).

图2.(a) and (c) Relationships between Raman frequencies and equivalent coordination number for WS2xSe2(1-x) and MoS2xSe2(1-x) monolayers. Figure 2 (b) and (d) Relationship between equivalent coordination number and doping concentration according to (a), (c).
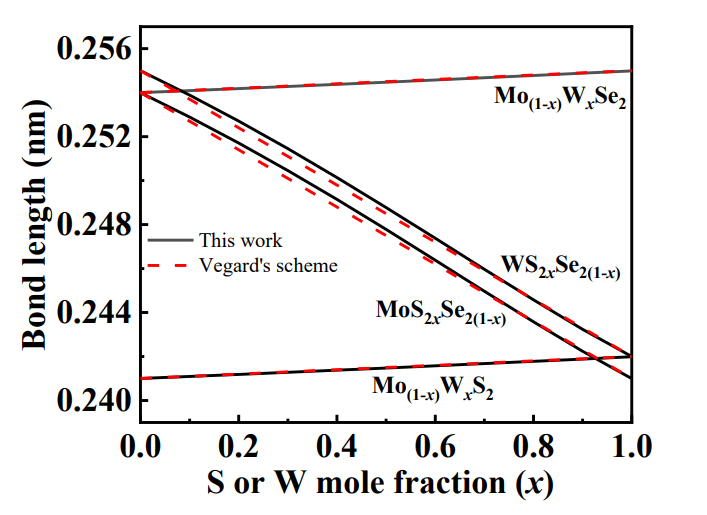
图3. Chalcogen atom S doping-induced bond length change for WS2xSe2(1-x) and MoS2xSe2(1-x); transition metal W doping-induced bond length change for Mo(1-x)WxSe2 and Mo(1-x)WxS2, showing the agreement between the calculated data from this work and the Vegard's scheme.
(审核责任人 伍建华)


